http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2010/09/linux-file-system-structure/
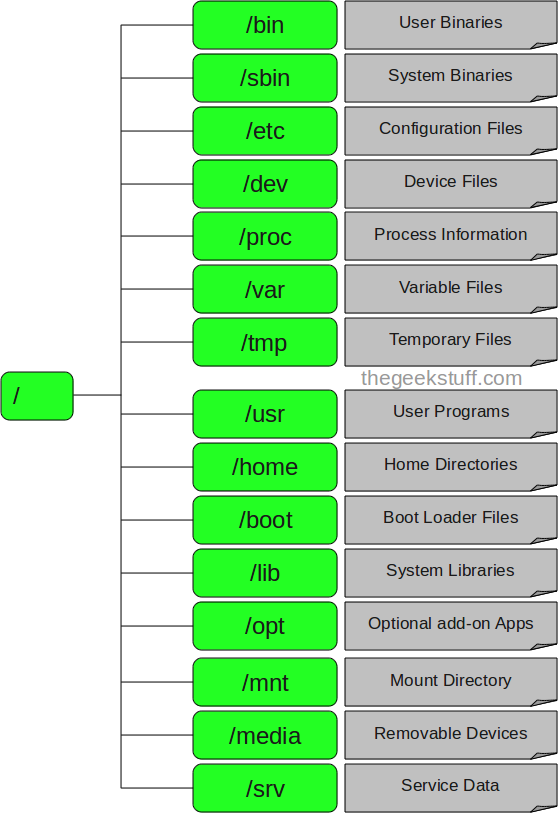
1. / – Root
- Every single file and directory starts from the root directory.
- Only root user has write privilege under this directory.
- Please note that /root is root user’s home directory, which is not same as /.
2. /bin – User Binaries
- Contains binary executables.
- Common linux commands you need to use in single-user modes are located under this directory.
- Commands used by all the users of the system are located here.
- For example: ps, ls, ping, grep, cp.
3. /sbin – System Binaries
- Just like /bin, /sbin also contains binary executables.
- But, the linux commands located under this directory are used typically by system aministrator, for system maintenance purpose.
- For example: iptables, reboot, fdisk, ifconfig, swapon
4. /etc – Configuration Files
- Contains configuration files required by all programs.
- This also contains startup and shutdown shell scripts used to start/stop individual programs.
- For example: /etc/resolv.conf, /etc/logrotate.conf
5. /dev – Device Files
- Contains device files.
- These include terminal devices, usb, or any device attached to the system.
- For example: /dev/tty1, /dev/usbmon0
6. /proc – Process Information
- Contains information about system process.
- This is a pseudo filesystem contains information about running process. For example: /proc/{pid} directory contains information about the process with that particular pid.
- This is a virtual filesystem with text information about system resources. For example: /proc/uptime
7. /var – Variable Files
- var stands for variable files.
- Content of the files that are expected to grow can be found under this directory.
- This includes — system log files (/var/log); packages and database files (/var/lib); emails (/var/mail); print queues (/var/spool); lock files (/var/lock); temp files needed across reboots (/var/tmp);
8. /tmp – Temporary Files
- Directory that contains temporary files created by system and users.
- Files under this directory are deleted when system is rebooted.
9. /usr – User Programs
- Contains binaries, libraries, documentation, and source-code for second level programs.
- /usr/bin contains binary files for user programs. If you can’t find a user binary under /bin, look under /usr/bin. For example: at, awk, cc, less, scp
- /usr/sbin contains binary files for system administrators. If you can’t find a system binary under /sbin, look under /usr/sbin. For example: atd, cron, sshd, useradd, userdel
- /usr/lib contains libraries for /usr/bin and /usr/sbin
- /usr/local contains users programs that you install from source. For example, when you install apache from source, it goes under /usr/local/apache2
10. /home – Home Directories
- Home directories for all users to store their personal files.
- For example: /home/john, /home/nikita
11. /boot – Boot Loader Files
- Contains boot loader related files.
- Kernel initrd, vmlinux, grub files are located under /boot
- For example: initrd.img-2.6.32-24-generic, vmlinuz-2.6.32-24-generic
12. /lib – System Libraries
- Contains library files that supports the binaries located under /bin and /sbin
- Library filenames are either ld* or lib*.so.*
- For example: ld-2.11.1.so, libncurses.so.5.7
13. /opt – Optional add-on Applications
- opt stands for optional.
- Contains add-on applications from individual vendors.
- add-on applications should be installed under either /opt/ or /opt/ sub-directory.
14. /mnt – Mount Directory
- Temporary mount directory where sysadmins can mount filesystems.
15. /media – Removable Media Devices
- Temporary mount directory for removable devices.
- For examples, /media/cdrom for CD-ROM; /media/floppy for floppy drives; /media/cdrecorder for CD writer
16. /srv – Service Data
- srv stands for service.
- Contains server specific services related data.
- For example, /srv/cvs contains CVS related data.
http://tldp.org/LDP/intro-linux/html/sect_03_01.html
Directory Content
/bin Common programs, shared by the system, the system administrator and the users.
/boot The startup files and the kernel, vmlinuz. In some recent distributions also grub data. Grub is the GRand Unified Boot loader and is an attempt to get rid of the many different boot-loaders we know today.
/dev Contains references to all the CPU peripheral hardware, which are represented as files with special properties.
/etc Most important system configuration files are in /etc, this directory contains data similar to those in the Control Panel in Windows
/home Home directories of the common users.
/initrd (on some distributions) Information for booting. Do not remove!
/lib Library files, includes files for all kinds of programs needed by the system and the users.
/lost+found Every partition has a lost+found in its upper directory. Files that were saved during failures are here.
/misc For miscellaneous purposes.
/mnt Standard mount point for external file systems, e.g. a CD-ROM or a digital camera.
/net Standard mount point for entire remote file systems
/opt Typically contains extra and third party software.
/proc A virtual file system containing information about system resources. More information about the meaning of the files in proc is
obtained by entering the command man proc in a terminal window. The file proc.txt discusses the virtual file system in detail.
/root The administrative user's home directory. Mind the difference between /, the root directory and /root, the home directory of the root user.
/sbin Programs for use by the system and the system administrator.
/tmp Temporary space for use by the system, cleaned upon reboot, so don't use this for saving any work!
/usr Programs, libraries, documentation etc. for all user-related programs.
/var Storage for all variable files and temporary files created by users, such as log files, the mail queue, the print spooler area, space for temporary storage of files downloaded from the Internet, or to keep an image of a CD before burning it.
No Comments