http://www.timetoolsglobal.com/2013/06/21/how-to-synchronize-microsoft-windows-to-a-ntp-server-1/
How To Synchronize Microsoft Windows to a NTP Server
Most modern operating systems, including Windows, can synchronize their system time to a NTP server. Windows utilizes a time service called ‘Windows Time’, which is automatically installed in the service list. The program executable is ‘w32time.exe’. The service is installed and enabled by default during installation.
Windows synchronizes time in different ways, depending on the network implementation utilized. When peer-to-peer networking is employed, each individual workstation sync to a time reference independently.
However, when Windows Domain Networking is deployed, only the Primary Domain Controller (PDC) synchronizes with a time reference. All other servers and workstations in the domain sync to the PDC using Windows proprietary protocol. The default installation procedure automatically configures workstations and servers to sync to the controlling PDC. Only the PDC needs to be configured to synchronize to an external time reference.
Configuring a Windows Server to Sync to an External Time Reference.
Applies to:
Microsoft Windows Server 2008
Microsoft Windows Server 2003
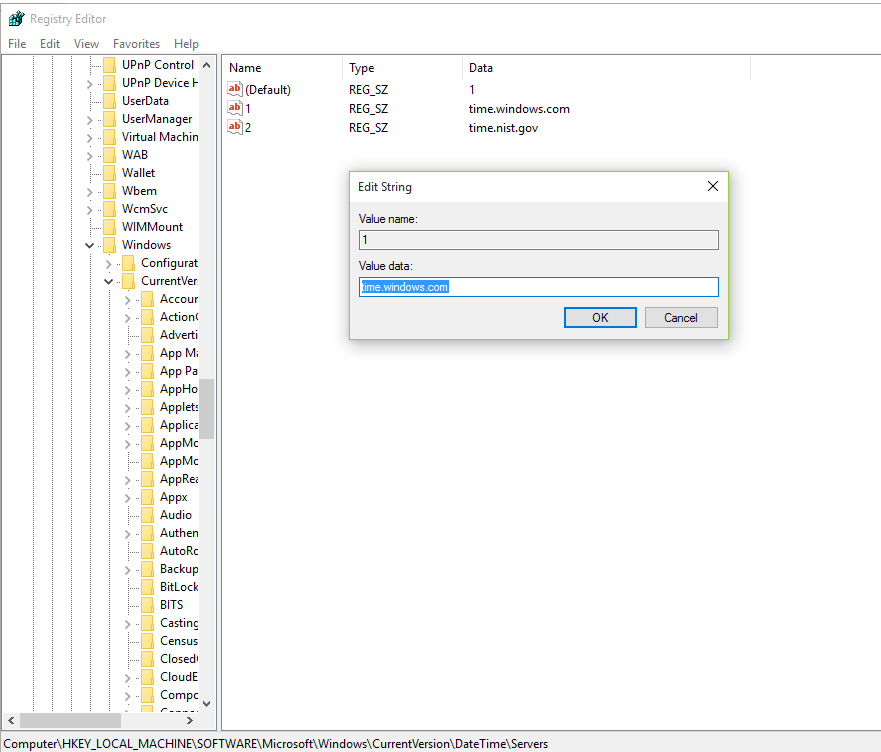
To configure a Windows PDC to synchronise with an external NTP server requires registry entry changes.
1. Change the server type to NTP.
Registry Key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Parameters\Type
Change value data to: NTP
2. Set announce flags.
Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Config\AnnounceFlags
Change value data to: 5
3. Enable NTP server
Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\TimeProviders\NtpServer
Change value data to: 1.
4. Specify the time sources.
Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Parameters
Change value data to: <peerlist>
< peerlist> is a list of space-delimited NTP peers from which time can be received. If DNS names are used, you must append ‘,0x1’ to each DNS name. Alternatively, a list of IP addresses can be specified.
5. Select poll interval.
Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\TimeProviders\NtpClient\SpecialPollInterval
Change value data to: <period>
< period> is the time in seconds between each poll. Microsoft recommends a value of 900, which equates to a polling frequency of once every 15 minutes.
6. Set the time correction settings.
These settings specify a time frame to validate time stamps received from an external reference. Only if the received timestamp falls between these registry settings will they be accepted. It provides a facility to reject timestamps that are too far away from the hosts system time. Microsoft recommends a setting of 1 hour (3600) or 30 minutes (1800).
Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Config\MaxPosPhaseCorrection
Change value data to: <seconds>
Where <seconds> is the maximum positive offset of the received time stamp from the system time.
Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Config\MaxNegPhaseCorrection
Change value data to: <seconds>
Where <seconds> is the maximum negative offset of the received time stamp from the system time.
7. Restart the windows time service.
Stop and restart the Windows Time Service using the ‘net stop’ and ‘net start’ commands:
net stop w32time && net start w32time
Synchronizing a Windows Workgroup
Applies to:
Microsoft Windows XP.
Microsoft Windows Vista.
Microsoft Windows 7.
When Windows for Workgroups is deployed, you have to manually configure time synchronization settings. You need to specify the time server that the Windows Time Service is to use as a reference clock. This is a very straightforward process; simply specify the time reference that the host is to synchronise with using the ‘net time’ command:
Net time \\<ntpserver> /set /yes
Where <ntpserver> is the DNS name or IP address of the time reference.
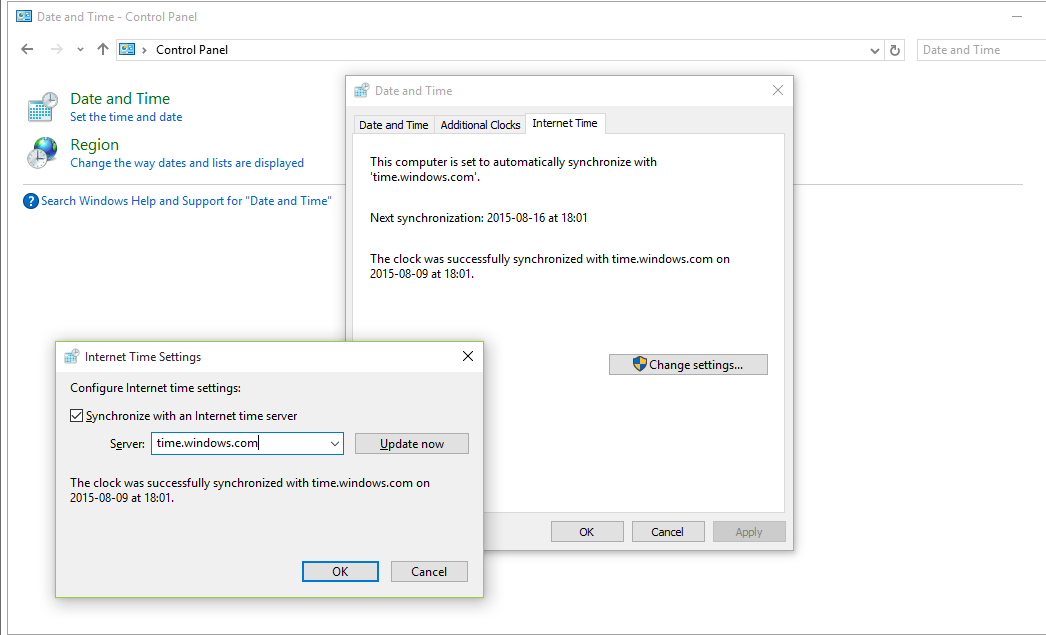
Alternatively, you can utilize the date and time properties applet from the control panel. Select the ‘Internet Time’ tab from the applet, check ‘Automatically Synchronize with an Internet Time Server’ and enter the DNS name or IP address of the server. If you select ‘Update Now’ the time service will attempt to contact and synchronise with the time reference immediately.
Where do I find the “Internet Time” (NTP) settings in Windows 10?
REGISTRY SETTINGS:
|
SpecialPollInterval : Explanation : Version : Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2003, and Windows Server 2008 NtpServer Explanation : Version : Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2008 UpdateInterval : Explanation : Version : Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2003, and Windows Server 2008 MinPollInterval : Explanation : Version : Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2003, and Windows Server 2008 |
No Comments